When development teams need to process thousands of file uploads daily across multiple applications, traditional polling-based monitoring systems create significant operational overhead and cost inefficiencies. Manual file-processing workflows can’t scale to meet modern application demands, leading to delayed processing, wasted resources, and potential data loss during peak loads.
Event-driven architecture solves this challenge by automatically triggering processing workflows the moment files arrive, scaling seamlessly from zero to thousands of concurrent operations while charging only for actual usage. This approach eliminates the need for continuous polling, reduces infrastructure costs, and provides instant processing with built-in observability.
In this note, we’ll learn how to build a production-ready, event-driven file-processing system using Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), AWS Lambda, and AWS CloudWatch, with Terraform automation. The architecture leverages AWS Key Management Service (KMS) for customer-managed encryption, structured logging, and enterprise-grade security controls, creating a fully automated pipeline that scales with demand.
Architecture Overview
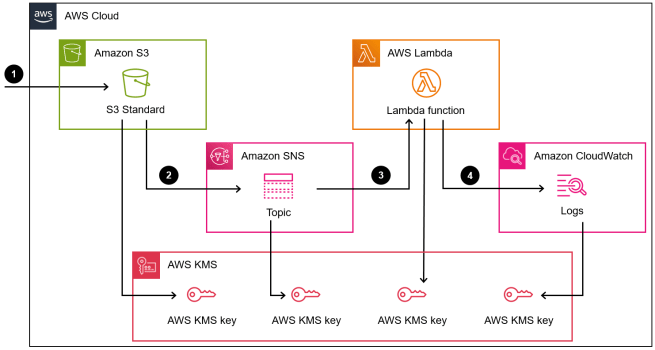
The event-driven workflow follows this sequence:
1. File uploaded to an Amazon S3 bucket triggers an event notification
2. Amazon SNS receives the notification with file metadata and event details
3. An AWS Lambda function processes the event payload and extracts file information
4. Amazon CloudWatch log captures structured logs for monitoring and troubleshooting
This high-level objective is further broken down into five implementation stages:
Stage 1: AWS KMS Encryption Setup for all services
Stage 2: Amazon S3 Bucket Configuration with event notifications
Stage 3: Amazon SNS Topic and AWS Lambda Integration
Stage 4: Amazon CloudWatch Logging and Monitoring
Stage 5: GitHub Actions Automation
Let us now delve into each of these stages. If you are interested and want to follow along, please refer to my GitHub repository: kunduso/aws-s3-sns-lambda-terraform.
Implementation
This Terraform configuration creates 27 AWS resources with zero security violations and follows enterprise best practices.
The project uses GitHub Actions for automated deployment, integrating secure AWS credentials via OpenID Connect (OIDC) to eliminate the need to store long-lived AWS credentials. For detailed OIDC setup instructions, see: securely-integrate-aws-credentials-with-github-actions-using-openid-connect.
Stage 1: AWS KMS Encryption Setup for all services
This stage implements a security-first approach using customer-managed KMS keys for all services. The architecture creates separate encryption keys for S3, SNS, Lambda, and CloudWatch to ensure complete security isolation between services while maintaining the event-driven workflow.
Step 1.1: Create AWS KMS keys and policies for each service
The following image shows the aws_kms_key and associated resources for Amazon S3 encryption.
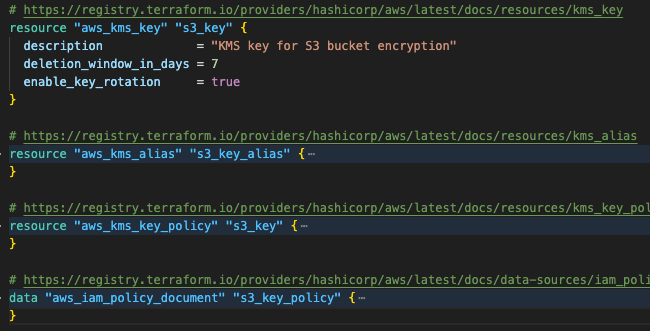
Each service receives its own dedicated encryption key with automatic rotation enabled and least-privilege key policies. The AWS KMS key policies are configured with granular permissions that include controlled cross-service access necessary for the event-driven workflow: Lambda requires decrypt permissions on both S3 and SNS keys to process encrypted event messages, while S3 needs access to the SNS key to publish encrypted notifications.
Stage 2: Amazon S3 Bucket Configuration
The S3 bucket serves as the entry point for the event-driven architecture, providing secure storage with comprehensive protection and event notification capabilities.
Step 2.1: Create the S3 bucket with encryption and versioning
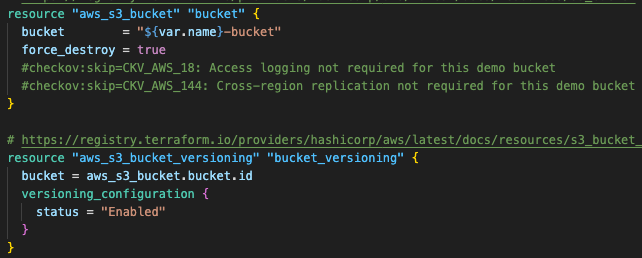
The S3 bucket provides secure storage through server-side encryption with customer-managed AWS KMS keys and versioning for data protection. Public access is completely blocked while lifecycle policies optimize costs by automatically cleaning up incomplete multipart uploads.
Step 2.2: Configure S3 event notifications
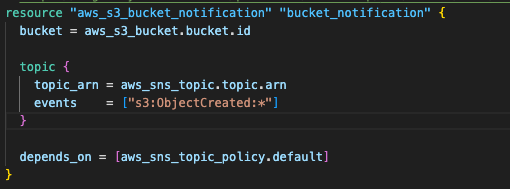
S3 event notifications are configured to trigger automatically when files are uploaded to the bucket. These notifications capture file metadata and send structured event payloads to SNS, enabling real-time processing without polling mechanisms.
Important Note: S3 buckets only support a single notification configuration resource in Terraform. Multiple aws_s3_bucket_notification resources targeting the same bucket will cause configuration conflicts. If you need multiple triggers, configure them within a single notification resource.
Stage 3: Amazon SNS Topic and AWS Lambda Integration
This stage creates the messaging infrastructure that connects S3 events to Lambda processing, ensuring reliable message delivery with encryption and proper IAM policies.
Step 3.1: Create an SNS topic with encryption
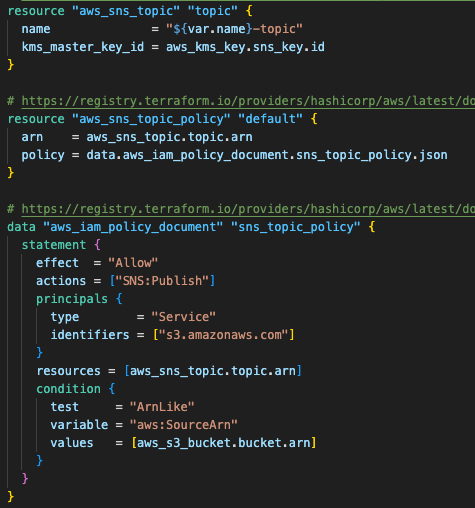
SNS provides a reliable message delivery system with an encrypted topic using customer AWS KMS keys. IAM policies allow S3 to publish events while maintaining security boundaries.
Step 3.2: Create an AWS Lambda function for S3 notification processing
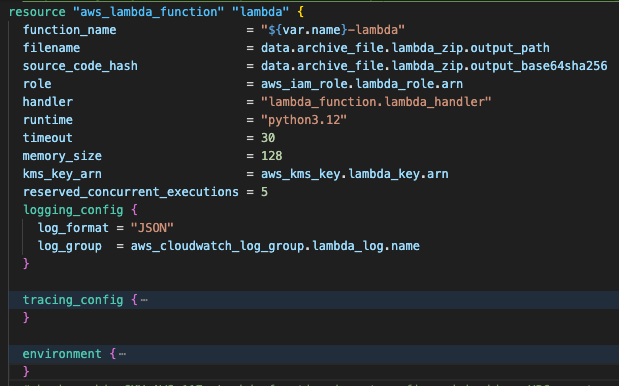
The Lambda function delivers serverless processing with Python 3.12 runtime and structured logging. Environment variables are encrypted with AWS KMS, X-Ray tracing provides observability, and concurrent execution limits ensure cost control.
Step 3.3: Configure SNS subscription to Lambda
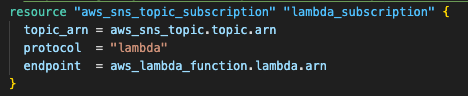
The SNS subscription enables automatic processing of incoming notifications, creating the bridge between S3 events and Lambda execution.
Stage 4: Amazon CloudWatch Logging and Monitoring
Comprehensive monitoring and audit trails are essential for production workloads, providing visibility into the entire event-driven pipeline.
Step 4.1: Create an Amazon CloudWatch log group with encryption
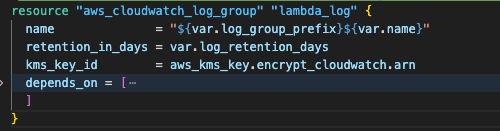
Amazon CloudWatch provides comprehensive monitoring and audit trails via encrypted log groups, using customer-managed AWS KMS encryption keys. The 365-day retention policy preserves logs, while the JSON structured format enables easy parsing and compliance reporting.
Stage 5: GitHub Actions Automation
To fully automate this deployment workflow, GitHub Actions orchestrates the entire process with secure AWS credential integration using OpenID Connect (OIDC). This approach eliminates the need to store long-lived AWS credentials as GitHub secrets.
Deployment Process
Once all the code is ready, it is deployed via GitHub Actions using the pipeline code in the .github/workflows folder. The workflow runs terraform apply only when changes are merged into the main branch, using OIDC authentication to obtain secure, temporary AWS credentials. This condition ensures that all infrastructure modifications are reviewed via pull requests, maintaining best practices for CI/CD and infrastructure-as-code.
This repository also includes a code-scanning pipeline using Checkov to ensure zero security violations by scanning Terraform configurations against hundreds of security best practices before deployment. For detailed implementation of Checkov with GitHub Actions, see: automate-terraform-configuration-scan-with-checkov-and-github-actions.
Deployment and Validation
After deployment, validate the event-driven pipeline by testing the complete workflow from file upload to log confirmation.
Step 1: Upload a test file
Upload a file to trigger the event-driven workflow either via the UI or using the AWS CLI: aws s3 cp test-file.txt s3://app-13-bucket/
Step 2: Verify processing in CloudWatch Logs
Check CloudWatch Logs at /aws/lambda/app-13 for the processing confirmation. You should see a structured JSON log entry similar to:
{
"timestamp": "2025-12-05T20:29:17Z",
"level": "INFO",
"message": "File uploaded: test-file.txt in bucket: app-13-bucket",
"logger": "root",
"requestId": "a7369b87-26aa-4ed9-964d-6ac53bdc3e15"
}
Step 3: Monitor performance metrics
Monitor Lambda execution metrics for:
– Execution time: ~10ms for typical file processing
– Memory usage: ~37MB average consumption
– Cold start: ~107ms for initial invocation
– Error rate: Should remain at 0% for successful processing
I captured the image below from the /aws/lambda/app-13 CloudWatch log after uploading a file to the app-13-bucket Amazon S3 bucket.

Conclusion
This serverless event-driven solution transforms file processing from manual, polling-based workflows into an automated, scalable solution. By combining Amazon S3, SNS, Lambda, and CloudWatch with Terraform automation, we learnt to create a production-ready system that (i) scales automatically with up to 5 concurrent file operations (configurable based on requirements), (ii) controls costs by eliminating continuous polling and charging only for actual usage, (iii) maintains security through end-to-end AWS KMS encryption and least-privilege access, and (iv) ensures reliability with comprehensive monitoring and structured logging.
The solution demonstrates how modern cloud-native patterns can deliver enterprise-grade capabilities while maintaining operational simplicity and cost efficiency.
